Fintech Expansion in Africa (2025): Moving Beyond Mobile Money Into a New Financial Era
For the past decade, Africa has been recognized as the global pioneer of mobile money. Services like M-Pesa in Kenya, MTN Mobile Money in West Africa, and Airtel Money across multiple regions revolutionized how people send, save, and spend. But in 2025, the continent’s fintech landscape has evolved far beyond simple money transfers. Africa is entering a new era of digital finance—one driven by artificial intelligence, blockchain, digital credit scoring, SME financing platforms, and integrated digital banking systems.
This transformation is not just creating convenience; it is changing the economic fate of millions. Today, fintech is powering small businesses, expanding access to credit, enabling cross-border trade, increasing financial inclusion, and strengthening consumer protection across the continent.
This article explores the major innovations pushing fintech beyond mobile money, the opportunities emerging for Africans, real-world success stories, challenges, and a forward-looking vision of Africa’s digital economy in 2030.
1. The Evolution of African Fintech: From Mobile Money to a Full Digital Economy
a. Mobile money laid the foundation
By providing a simple way to store and move money using feature phones, mobile money created the infrastructure and trust required for more advanced digital financial services.
b. Fintech is now solving deeper economic challenges
In 2025, fintech platforms address:
- Access to credit
- Small business financing
- Insurance distribution
- Investment access
- Cross-border payments
- Financial literacy
- Digital identity verification
This shift marks a transition from transaction tools to economic empowerment solutions.
c. Adoption is accelerating
With over 600 million smartphone users in Africa and rapidly expanding internet access, digital financial services are reaching even the most remote communities.
2. Key Fintech Innovations Reshaping Africa in 2025
a. Digital Credit Scoring & AI-Powered Lending
Traditional banks often avoid lending to individuals or small businesses who lack collateral or formal credit history. AI has changed this.
Modern digital lenders analyze:
- Mobile money transactions
- Utility payments
- Smartphone usage patterns
- Social behavior data
- Business revenue flows
This creates alternative credit scores, enabling millions of previously “unbankable” Africans to access loans.
b. SME Financing Platforms
Africa’s small businesses power over 80% of employment, but financing has always been a challenge.
Today’s fintech platforms offer:
- Invoice financing
- Merchant cash advances
- Inventory loans
- Revenue-based financing
These tools help small enterprises grow without dealing with bank bureaucracy.
c. Blockchain for Remittances & Trade
Remittances are a lifeline for many African households. Blockchain-based platforms reduce transfer fees and settlement times.
Other uses include:
- Verifying trade documents
- Tracking imports/exports
- Tokenized assets (real estate, commodities)
- Secure cross-border payments
Blockchain increases transparency and reduces fraud—critical for Africa’s growing trade ecosystem.
d. Digital Insurance (Insurtech)
Insurance penetration in Africa has always been low. Fintech is changing that through:
- Micro-insurance via mobile money
- Pay-as-you-go health and crop coverage
- Automated claim payouts using AI
- Weather-indexed agricultural insurance
These products protect farmers, small businesses, and families from unexpected shocks.
e. Virtual Banks & Neobanking
Neobanks are offering:
- Zero-fee accounts
- Instant virtual cards
- Budgeting tools
- Savings plans
- High-yield digital wallets
These banks appeal to young Africans who prefer digital-first financial services.
f. RegTech & Fraud Prevention
Regulatory technology systems help financial institutions detect:
- Identity fraud
- SIM-swap attacks
- Money laundering
- Unusual transaction patterns
AI-powered security is becoming essential as digital payments grow.
3. Regional Success Stories Driving Fintech Growth
a. East Africa: The world’s most mature mobile-first economy
Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda continue to lead in mobile-money innovation. In 2025:
- AI-driven microloans
- Virtual savings groups
- Digital wealth tools
- Insurance through mobile money
…are becoming mainstream.
Kenya’s fintech ecosystem remains the benchmark for financial inclusion globally.
b. West Africa: Nigeria and Ghana powering the next wave
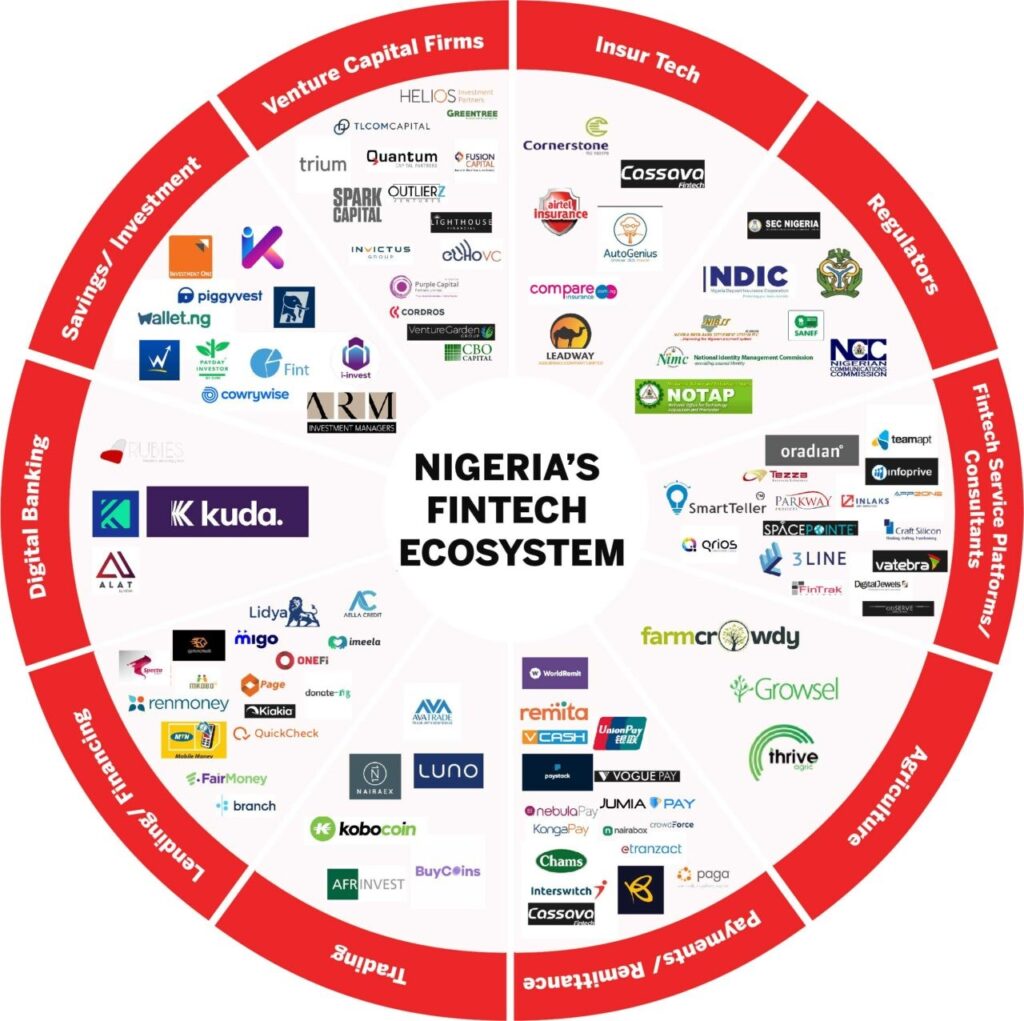
Nigeria is the continent’s fintech capital, with startups offering:
- Digital banks
- Crypto payments
- Lending apps
- B2B fintech infrastructure
Ghana, meanwhile, is pioneering mobile money interoperability, enabling seamless cross-network transactions.
c. Southern Africa: Advanced payments infrastructure
South Africa leads in:
- Online payments
- POS systems
- B2B financial tools
- Digital insurance
Botswana and Namibia are also adopting cross-border mobile money systems.
d. Francophone Africa: Rapid adoption of mobile-first banking
Countries like Côte d’Ivoire, Senegal, and Mali rely heavily on mobile wallets. Fintech apps are enabling trade, agriculture payments, and youth entrepreneurship.
4. How Fintech Is Benefiting African Individuals & Businesses
a. Financial inclusion is expanding
Millions of Africans now hold digital wallets rather than physical bank accounts. This allows them to:
- Save easily
- Transact instantly
- Access loans
- Receive payments
b. Small businesses are becoming more resilient
Digital tools help businesses:
- Track sales
- Manage inventory
- Accept digital payments
- Apply for credit automatically
SMEs now have clear financial records, making them more competitive.
c. Cross-border commerce is growing
Fintech is enabling:
- Intra-African trade
- Freelancing income from abroad
- E-commerce expansion
This supports the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) vision.
d. Households gain financial stability
With micro-insurance and savings tools, families can better manage emergencies and long-term planning.
e. Youth entrepreneurship is exploding
Africa’s young population is using fintech platforms to launch:
- Online stores
- Food delivery services
- Freelance digital services
- Social commerce brands
Fintech lowers entry barriers and accelerates digital innovation.
5. Government Policies Supporting Fintech Growth
Many African governments now recognize fintech as a growth engine.
a. Regulatory sandboxes
Countries like Kenya, Rwanda, and Nigeria allow fintech startups to test innovations under government supervision.
b. Digital ID systems
National ID programmes enable secure onboarding and reduce fraud.
c. Open banking frameworks
Some countries are implementing systems that allow financial data sharing—boosting competition and innovation.
d. Strengthening cybersecurity laws
Protecting consumers is a priority as digital payments grow.
e. Supporting cross-border payment integration
Regional blocs aim to make African payments faster and cheaper.
6. Major Challenges Facing African Fintech in 2025
Despite the progress, several obstacles remain.
a. Fraud and cybercrime
Growing digital adoption makes fintech platforms attractive targets for cybercriminals.
b. Regulatory inconsistencies
Different countries have different rules, which complicates cross-border expansion.
c. Customer trust issues
Some consumers fear scams or hidden fees, making adoption slower in rural areas.
d. High mobile data costs
In some countries, data is still too expensive for constant fintech usage.
e. Funding volatility
Global economic uncertainty has affected startup investments, slowing some fintech expansion plans.
7. The Future of African Fintech by 2030
If current momentum continues, Africa may become one of the world’s most dynamic digital finance ecosystems.
a. Fully digital banks dominating the market
Neobanks could compete directly with traditional banks, offering faster and cheaper services.
b. AI-driven personal financial assistants
Apps will automatically help users save, invest, and budget in real time.
c. Borderless African payment networks
Sending money from Ghana to Kenya could become as easy as sending a text message.
d. Tokenized assets and digital currencies
Blockchain-based property titles, commodities, and government-backed digital currencies may become common.
e. Micro-enterprise boom
E-commerce, freelancing, and gig work will explode as fintech lowers financial barriers.
Conclusion: Africa’s Fintech Evolution Is Redefining the Continent’s Economic Future
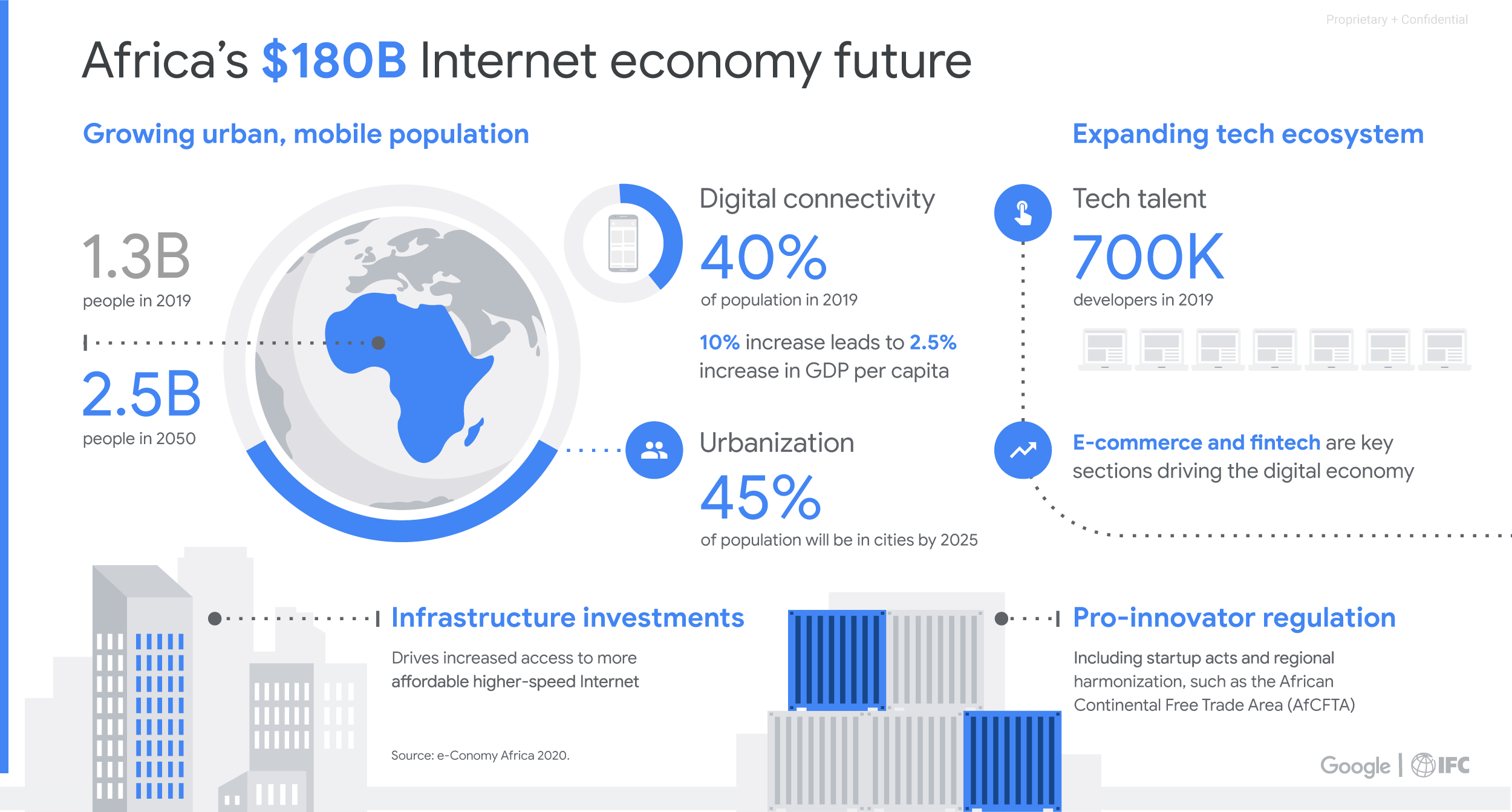
In 2025, Africa’s fintech sector has grown far beyond mobile money. It is now driving economic development, empowering small businesses, enhancing financial inclusion, and reshaping how money flows within the continent. The world is watching Africa not as a follower, but as an innovator—building systems that are faster, cheaper, and more inclusive than many developed countries.
Fintech is no longer a convenience—it is a catalyst for social and economic transformation.